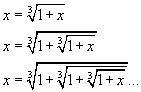
From the plastic equation you have
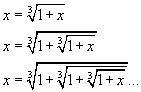
that is
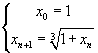
With a pocket calculator you get the following approximate values
| 1.0 |
| 1.259921049894873 |
| 1.3122938366832888 |
| 1.3223538191388249 |
| 1.324268744551578 |
| 1.3246326252509202 |
| 1.3247017485103587 |
| 1.3247148784409506 |
| 1.324717372435671 |
| 1.3247178461621454 |
| 1.324717936144965 |
It is possible to obtain more interesting sequences of rational terms.
If you write the plastic equation in the following way
![]()
you can define the sequence
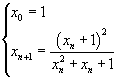
that is
| fraction | decimal approximation |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1.0 |
| 4 / 3 | 1.33333333333333333333... |
| 49 / 37 | 1.3243243243243243243... |
| 7396 / 5583 | 1.3247358051226938922... |
| 168454441 / 127162573 | 1.3247171477098060921 |
Applying the Newton's method to approximate the real zero of the function
![]() you have
you have
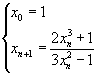
that is
| fraction | decimal approximation |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1.0 |
| 3 / 2 | 1.5 |
| 31 / 23 | 1.3478260869565217391... |
| 71749 / 54142 | 1.32520039895090687451... |
| 448712783118393 / 338723203112569 | 1.3247181739990537344... |