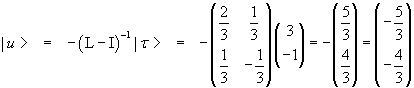Since both linear transformations and translations are bijective transformations, also their compositions are bijective transformations.
The composition of a linear transformation with a translation is said affine transformation.
An affine transformation can be algebraically expressed in the following way:
![]()
The vector v'(x’;y’) which corresponds to the vector v(x;y) is done by
The same procedure can be more synthetically expressed by the matrical equation
![]()
The inverse transformation expresses v in terms of v’. One obtains
![]()
Affine transformations preserve all the properties of geometric linear transformations.
Example.
The affine transformation
![]()
is done by the composition of the linear transformation
![]() with the
translation
with the
translation
![]()
The determinant of L is Δ = - 3; the inverse of L is
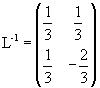
So we obtain
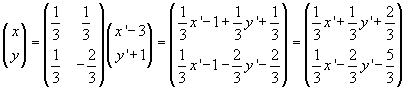
The same result is expressed by algebraic system
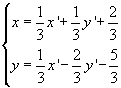
A fixed point of a transformation T is a point that is mapped to itself.
The fixed point u of an affinity done by the composition of L and τ can be determined by solving the equation
![]()
that is
![]()
In the given example we have
![]()
The inverse matrix of (L-I) is
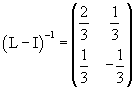
The opposite of the product between this inverse matrix and |τ> gives the fixed point: