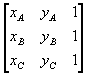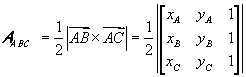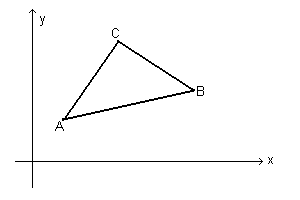
If you know the basics of vector calculus, you can easily deduce the expression of the area of a triangle given the coordinates of the vertices, noting that the magnitude of the vector cross product can be geometrically interpreted as the area of the parallelogram obtained by applying the arrow representations of the two vectors to the same point and drawing the parallel lines througt the head of each vector to the other vector.
We can therefore conclude that the area of the triangle identified by two vectors coincides with half the magnitude of their cross product.
Given, in the orthogonal Cartesian plane Oxy, the triangle ABC
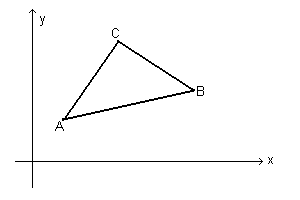
the sides AB and BC can be interpreted as vectors
![]()
![]()
Their cross product is
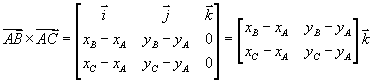
If we expand the determinant
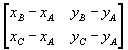
we see that it is equivalent to the determinant