


|  |
|
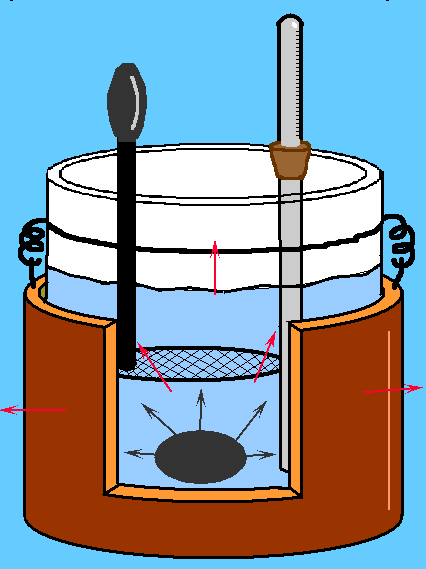
The calorimeter of Regnault (or of mixtures) is an instrument that it allows to measure the amounts of heat yielded or absorbed from a substance or a body during a physical or chemical process, and the thermal property of the substances (specific heat, heats of combustion,..).
|
|
|
The observations on the thermal exchanges carry to the considerations that the increasing of the amount of heat yielded from a body increase its temperature;if two bodies of the same substance, but different mass, maintain the same temperature, they yield two various amount of heat (in particular the object biggest yields more heat), and therefore to equality of conditions, the quantity of heat yielded from a body depends on the nature of the same body. The specific heat is a specific property of the substances and it can be found through the following espression:
where Q is the heat yielded from the body of mass m when the temperature diminishes of Δt degrees, and c is a constant characteristic of the considered substance, that is the SPECIFIC HEAT of the body .
Considering inside of the instrument a water amount (ma), its temperature, called tf, is approximately 20°C. Moreover we used an object, whose mass is mc and whose temperature is tc.
where te indicates the temperature of equilibrium to the term of the exchange of heat between the champion and the water. Moreover we know that the specific heat of the water is 1; therefore the formula will be reduced to The heat yielded from the champion will be instead
According to the second principle of thermodynamic, the heats correspond to the same value therefore is possible campair all the two expression Isolating the specific heat of the champion we will obtain: |
|
THE WATER MASS EQUIVALENT TO THE CALORIMETER